CNC Routing vs CNC Milling: What’s the Difference?
You’d be unlikely to walk into a modern workshop, automotive plant, aerospace facility, or electronics factory without spotting a CNC router or CNC milling machine hard at work. These machines, powered by computer numerical control, have become the backbone of today’s manufacturing, making it possible to create parts that are both highly accurate and tailored to specific designs.
However, while CNC routers and CNC mills may appear similar at first glance, they each bring different strengths to the table. In this article, we’ll walk through how these machines work, highlight their advantages and limitations, and help you understand which one is best suited for different projects and industries.
What is CNC Machining?
CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control. It means using computer software to control machine tools with very high accuracy. Instead of manually guiding tools, the computer follows a programmed design, which makes the work faster, more precise, and more consistent.
CNC machining is used in almost every industry today: automotive, aerospace, electronics, woodworking, and even medical equipment. Read in more detail about CNC Machining, its working, and its wide applications where it is commonly used.
What is CNC Milling?
A CNC milling machine is designed for cutting hard materials like steel, aluminum, and titanium. It uses a rotating tool to remove material from a block, layer by layer.
- Working principle: The material is clamped to the table while the rotating tool moves in multiple directions (X, Y, Z axes).
- Structure: Mills are heavy, rigid, and built with strong frames to handle the cutting forces.
- Tooling setup: Uses different types of cutting tools like end mills, face mills, or drills.
- Projects: Perfect for aerospace components, automotive parts, molds, dies, and complex mechanical pieces.
Read in more detail about CNC milling machining, its uses, and working principle. For high-quality precision milling solutions, Kirmell offers professional CNC machining services to meet your project needs.

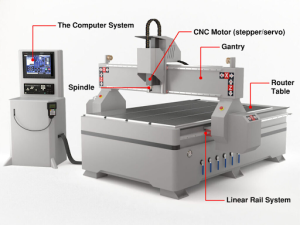
What is a CNC Router?
A CNC router is lighter and faster. It is mostly used for cutting wood, plastic, foam, and soft metals like aluminum. Routers are great for shaping large sheets and making creative designs.
- Working principle: The cutting head moves over a large flat table where the material is placed.
- Structure: Usually lighter in weight compared to mills.
- Tooling setup: Equipped with router bits rather than milling cutters.
- Projects: Ideal for sign-making, furniture, cabinetry, and decorative panels.
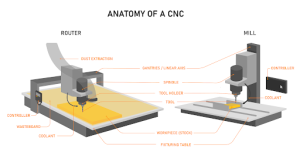
CNC Milling Machine vs. CNC Router: A Quick Comparison
Here’s a quick side-by-side look at how they compare:
| Feature | CNC Router | CNC Mill |
| Speed | Very fast, cuts quickly | Slower but more powerful |
| Materials | Best for wood, plastics, soft metals | Best for hard metals & tough materials |
| Accuracy | Good, but limited on harder materials | Excellent precision and tolerance |
| Cutting Area | Large, flat sheets | Smaller, detailed, 3D shapes |
| Cost | Usually cheaper | More expensive |
Key Differences Between CNC Routers and CNC Mills
Accuracy & Precision
CNC routers provide good accuracy when working with softer materials like wood, foam, and plastics. However, they can struggle to hold tight tolerances on harder metals. This makes them suitable for projects where speed and shape matter more than extremely fine detail.
On the other hand, CNC mills are built for extreme precision. They can consistently achieve very tight tolerances, which is why industries such as aerospace and automotive rely on them for parts where even a small error can cause major issues.
Material Compatibility
Routers are best for materials such as wood, foam, plastics, and soft metals like aluminium. They are excellent for creative designs, decorative work, and large sheets.
Mills, however, can handle much harder materials. They are designed to cut steel, titanium, aluminium alloys, brass, and other metals with ease, while also working on plastics and composites when needed.
Cutting Area & Size
A CNC router generally has a large cutting area, which allows it to handle full sheets of material. This is why they are commonly used in woodworking, cabinetry, and signage.
Mills, on the other hand, have a smaller working envelope but make up for it by enabling complex 3D cuts and detailed features that routers cannot easily achieve.
Speed & Efficiency
Routers are designed for speed and high-volume production. They can move quickly across large surfaces, making them highly efficient for cutting and shaping softer materials.
Mills are slower, but their power and durability allow them to cut through tough metals without losing accuracy, even during long production runs.
Power & Rigidity
Routers are relatively lightweight in construction. While this makes them more affordable and easier to operate, it also means they lack the strength required for heavy-duty machining.
Mills are rigid, heavy machines. Their robust frames are built to withstand strong cutting forces, making them ideal for precise and demanding metalwork.
Tooling Options
Routers typically use router bits, which are suitable for shaping wood, plastics, and softer metals. Their tooling options are somewhat limited compared to mills.
Mills support a wide variety of cutting tools, including drills, end mills, and face mills. This allows for more flexibility in machining operations, from simple drilling to complex shaping.
Component Type
Routers are perfect for producing artistic, decorative, or large parts, such as furniture panels, signage, and design pieces. They excel in industries where creativity and speed matter most.
Mills, in contrast, are built for engineered mechanical parts that require strength and precision, such as engine components, aerospace brackets, and moulds.
Costs & Maintenance
Routers are usually less expensive to purchase and maintain. They also consume less power and are easier for beginners to learn.
Mills come with a higher cost and often require more maintenance. However, they also last longer, can handle tougher materials, and deliver a higher return on investment for industries that demand precision.
Applications of CNC Mills vs. CNC Routers
- Industrial Manufacturing: CNC mills are widely used in industrial settings to produce accurate metal parts. These parts often serve as critical components in machines, engines, and heavy equipment.
- Aerospace & Automotive: When safety and accuracy are non-negotiable, CNC mills take the lead. They are capable of producing high-precision components for aircraft, vehicles, and other transportation systems where reliability is essential.
- Furniture & Woodworking: CNC routers shine in woodworking and furniture production. From cabinetry to carved panels and decorative elements, routers allow manufacturers to shape wood and other softer materials quickly and creatively.
- Prototyping: Both routers and mills are useful in prototyping, depending on the material and design complexity. Routers are excellent for quick, large-scale mock-ups, while mills are best for detailed, functional prototypes made from metals or strong plastics.

Factors to Consider When Choosing
Budget
CNC routers cost less than CNC mills, making them a good choice for wood, plastics, or light materials. Mills are more expensive but worth the investment when high accuracy and durability are required.
Type of Material
If your projects involve wood, plastics, foam, or composites, routers are more practical. For steel, titanium, brass, or aluminium alloys, a CNC mill is necessary due to its strength and rigidity.
Production Volume
Routers excel at fast, high-volume sheet cutting, especially for wood or plastic. Mills are slower but ideal for lower-volume jobs where consistent accuracy and part quality are critical.
Tolerance & Precision
Routers provide good accuracy for softer materials, but mills deliver the tight tolerances needed for aerospace, automotive, and industrial-grade components.
Workshop Setup
Routers are lighter and easier to set up. Mills are heavier, need more space and power, and require a stronger foundation to prevent vibration.
At Kirmell, we guide clients in selecting the right process, whether CNC routing for speed and sheet work or CNC milling for precision and metals, ensuring every project gets the best fit.

Common Misconceptions
- “Routers can’t cut metals.”
Routers can cut aluminium and other soft metals, but only for light jobs. For stronger metals like steel or titanium, a CNC mill is the proper choice.
- “Mills are always slow.”
Mills are slower because they focus on precision, but modern mills are faster with advanced tooling. They balance accuracy with efficiency in demanding industries.
- “Routers are only for woodworkers.”
Routers are popular in woodworking but also widely used in sign-making, plastics, and light aluminium projects, showing they are versatile machines.
Expert CNC Milling & Routing Solutions by Kirmell
At Kirmell, we specialise in providing professional CNC machining services that cover both milling and routing. Our team is equipped to handle a wide variety of projects, from precision metal parts and durable prototypes to custom wooden components and large-scale sheet cutting.
By combining advanced equipment with expert knowledge, we deliver results that are accurate, efficient, and tailored to your specific requirements. Whether you’re looking for one-off prototypes, small production runs, or large-scale manufacturing, Kirmell has the skills and experience to bring your designs to life.
Ready to start your next project? Contact Kirmell today to discuss your machining needs and see how we can support your goals.
Conclusion
Both CNC routers and CNC mills are incredibly powerful tools in modern manufacturing, but they serve different roles. A CNC router is the best choice if your priority is speed, working with large sheet materials, or focusing on wood, plastics, and lighter projects. Its ability to cut quickly across broad surfaces makes it perfect for woodworking, signage, and creative design work.
A CNC mill, on the other hand, is ideal if you require high accuracy, strength, and the ability to handle metals. Mills excel in producing small, detailed, and highly engineered parts where precision is critical, such as in the aerospace, automotive, and medical industries.
FAQs
What is CNC routing?
What is CNC milling and how is it different from CNC routing?
What’s the difference between a CNC router vs CNC cutter?
How do I choose between the CNC routing process and the CNC milling process?
Why should I choose Kirmell for CNC machining services?




Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!