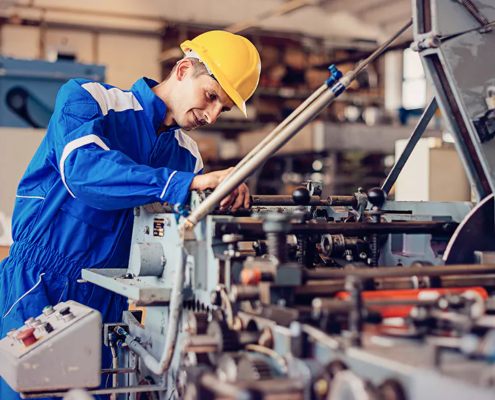

Laser Cutting Safety Basics: What Risks to Know About
Laser cutting has transformed modern manufacturing. From precision…
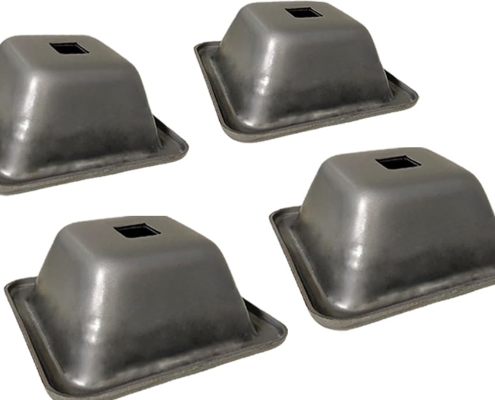

Round vs Square Pallet Feet: Which One Should You Use
When choosing pallet feet for steel pallets and stillages, one…
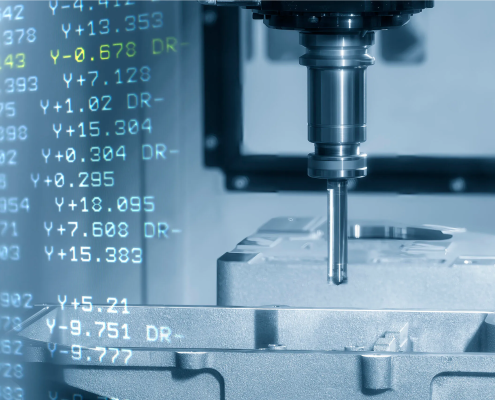

G-Code vs M-Code: Understanding Their Roles in CNC Machines
CNC machining is at the heart of modern manufacturing. From precision…
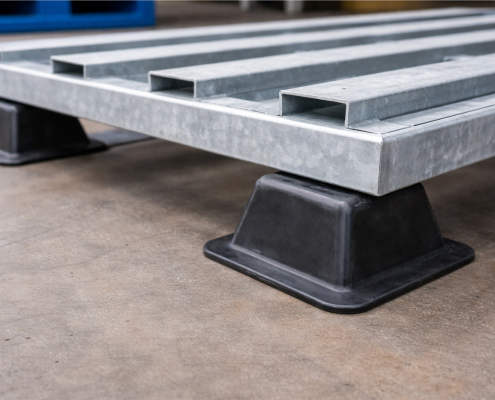

How to Choose the Right Pallet Feet for Steel Pallets and Stillages
When selecting pallet feet for steel pallets and stillages, the…
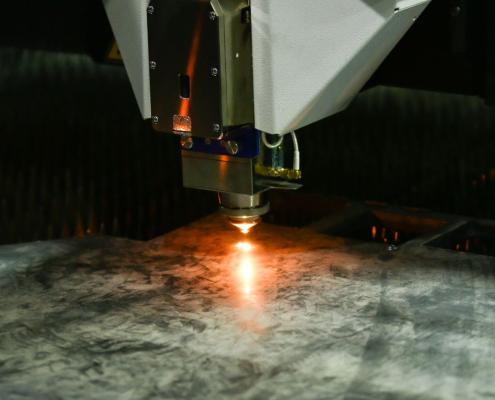

Nitrogen vs Oxygen in Laser Cutting: What’s the Difference?
Laser cutting looks simple from the outside: a focused beam melts…
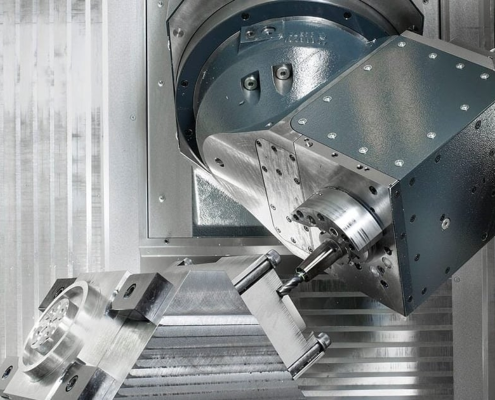

Which Is Better: 3-Axis or 5-Axis CNC Machining?
When it comes to CNC machining, one of the most common questions…
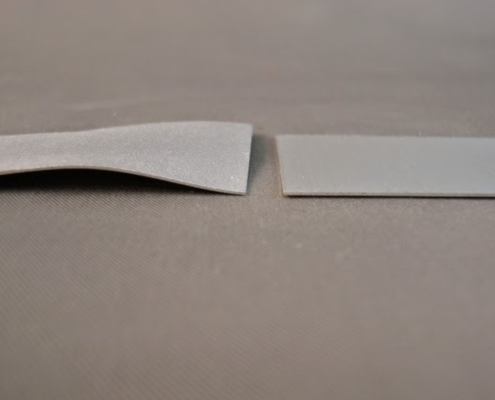
How to Reduce Warping in Laser-Cut Sheet Metal
Warping is one of the most common and frustrating problems in…
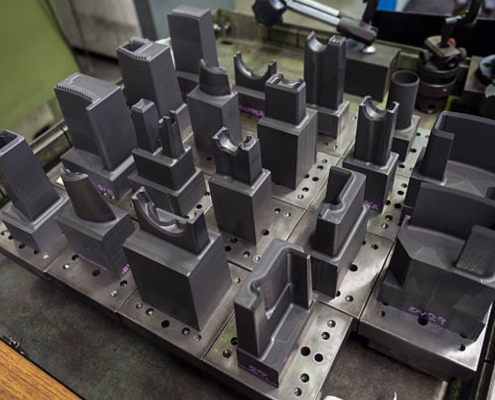
What Is Fixturing in CNC Machining and Why Does It Matter?
In modern manufacturing, CNC machining is one of the most trusted…
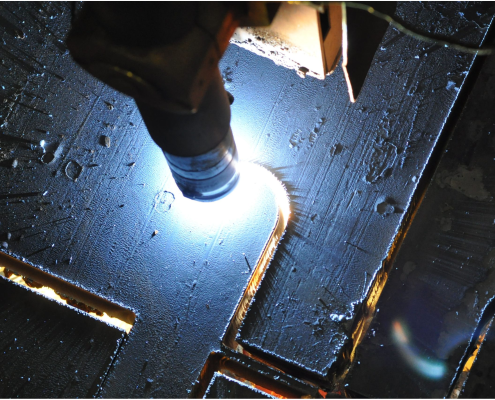
What Is Dross in Laser Cutting and How Do You Remove It?
Dross is the unwanted, re-solidified metal that sticks to the…
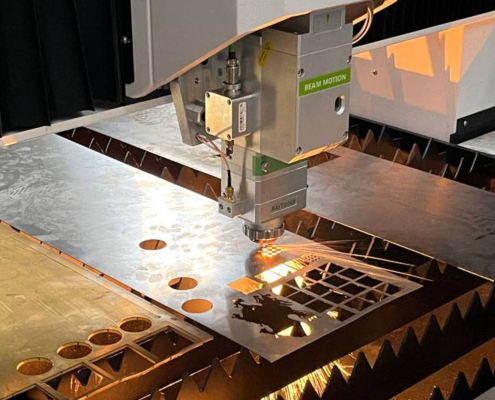

What Is Laser Kerf and Why Does It Matter?
Laser cutting looks “perfect” from the outside: you draw…
