CNC Grinding Machines: Precision Finishing for Complex Parts
In today’s advanced manufacturing world, creating complex parts with flawless finishes and extreme accuracy is no longer optional; it’s essential. From aerospace engines to medical implants, industries rely on technologies that can deliver parts with the tightest tolerances and smoothest surfaces. This is where CNC grinding machines stand out. They are purpose-built for shaping, refining, and perfecting parts that traditional machining methods can’t handle on their own.
This blog explores the working principles, machine types, advantages, and applications of CNC grinding machines, offering a complete guide to how they deliver precision finishing for complex parts.
What is CNC Grinding?
Put simply, CNC grinding is a subtractive manufacturing technique that uses a rotating grinding wheel to remove material from a workpiece. Unlike milling or turning, grinding achieves extremely fine finishes and tight tolerances. It’s particularly valuable when working with hardened materials like steel or ceramics, where cutting tools wear out quickly.
Think of it as the perfect combination of automation, computer-controlled accuracy, and the abrasive power of grinding wheels. The result: parts that meet the most demanding performance standards.
Additionally, explore our other blogs on CNC Milling and CNC Machining to gain a deeper understanding of these related technologies and their operational principles.
Kirmell offers CNC grinding services to deliver precise, smooth, and reliable results for complex parts. Contact us today to discuss your project or request a free quote.

Core Components of a CNC Grinding Machine
Although designs vary depending on the manufacturer and application, most CNC grinding machines share several key components that work together to ensure precision and repeatability.
Grinding Wheel
The grinding wheel is the primary cutting tool of the machine. Made from abrasive materials such as aluminium oxide, silicon carbide, or diamond, it rotates at high speeds to remove material in extremely fine increments. The choice of wheel depends on the material being ground and the desired surface finish.
Splash Guard
The splash guard surrounds the work area to contain coolant and debris during grinding. This not only keeps the workspace clean but also enhances operator safety by preventing sparks, chips, and coolant from spreading.
Column
The column supports the spindle and grinding wheel assembly. It provides the vertical movement (Z-axis) necessary to bring the wheel into contact with the workpiece. A rigid column ensures stability and reduces vibrations.
Coolant Nozzle
The coolant nozzle delivers a steady stream of coolant to the grinding zone. Coolant reduces heat, prevents damage to both wheel and workpiece, and flushes away chips for a smoother finish and longer tool life.
X-, Y-, and Z-Axis Handwheels
These manual handwheels allow the operator to adjust the position of the table or grinding wheel along the X, Y, and Z axes. Even though CNC machines are automated, handwheels are useful for setup, calibration, and fine adjustments.
Coolant Tank
The coolant tank stores and circulates the coolant used in the grinding process. It typically includes pumps and filters to maintain coolant quality, ensuring efficient heat dissipation and chip removal.
Saddle
The saddle sits between the base and the work table, allowing controlled movement of the table along a specific axis (usually the Y-axis). It plays a crucial role in positioning accuracy.
Electrical Cabinet
The electrical cabinet houses the electronic components, drives, and wiring that power and control the CNC machine. It connects to the CNC control unit and ensures safe, reliable operation.
Grinding Wheel & Coolant Controls
Located near the operator’s panel, these controls allow adjustments to grinding wheel speed, feed rates, and coolant flow. They provide flexibility to fine-tune the grinding process for different materials and finishes.

How Does CNC Grinding Work?
The CNC grinding process combines abrasive action with advanced computer automation to achieve extremely fine tolerances.
Programming
Operators or engineers use CAD/CAM software to create digital blueprints of the part. The software defines the grinding path, tool movement, feed rates, and other variables. This ensures the machine follows the exact specifications required for the final product.
Setup
Once the program is loaded, the workpiece is clamped securely into the workholding system. The grinding wheel is mounted, balanced, and aligned to the required position, preparing the machine for operation.
Grinding Operation
During operation, the grinding wheel rotates at very high speeds while coming into contact with the workpiece. Instead of removing large chunks of material, it shaves off tiny amounts with each pass. This gradual approach allows for extremely tight tolerances.
Precision & Control
Modern CNC grinders are equipped with sensors and feedback systems that monitor force, wheel wear, and part alignment in real time. These systems automatically adjust movements and speeds to maintain accuracy.
Finishing
The result of the process is a part with precise geometry and a smooth surface finish that often requires no further machining. This makes grinding ideal for final finishing steps in critical industries.
Kirmell’s CNC grinding services apply this process with advanced software and precision setups, ensuring every project meets strict accuracy and finish requirements.
Types of CNC Grinding Machines & Processes
Grinding is not a one-size-fits-all process. Different machine types and techniques are used depending on the geometry, material, and required finish.
Surface Grinding
This method produces flat, smooth surfaces. It is commonly used to create reference planes, tool plates, and parts that require parallelism and flatness. Both horizontal and vertical spindle configurations are available.
Cylindrical Grinding
Cylindrical grinders handle parts like shafts, rods, and tubes. They can grind external surfaces (external cylindrical grinding) or internal bores (internal cylindrical grinding), making them versatile for automotive, aerospace, and industrial components.
Centerless Grinding
Unlike cylindrical grinding, centerless grinding doesn’t use centres to hold the part. Instead, the workpiece rests between a regulating wheel and a grinding wheel. This method is excellent for the continuous production of cylindrical parts such as bearings, pins, and rollers.
Jig Grinding
Jig grinding is designed for creating precision holes, complex contours, and intricate geometries. It is often used in tool and die making, where accuracy at the micron level is required.
Universal Internal Grinding
This type of grinder provides flexibility for machining various internal geometries. It’s widely used when parts require different bore diameters, steps, or tapers within a single workpiece.
Specialised Techniques
Certain applications require unique grinding solutions, such as gear grinding or thread grinding. These specialised machines are built to handle highly specific shapes with extreme precision.
Hybrid Approaches
In some advanced manufacturing setups, grinding is combined with other processes like electrical discharge machining (EDM). These hybrid approaches enhance capabilities, reduce setup time, and enable manufacturers to handle complex geometries within a single system.
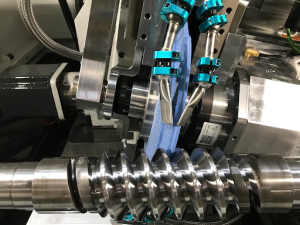
What Materials Can Be Processed with CNC Grinding?
One of the biggest strengths of CNC grinding is its ability to handle a wide range of challenging materials. While other machining methods may struggle with tool wear, heat, or poor finishes, CNC grinding excels thanks to its abrasive cutting process and precision.
1. Metals
Grinding is widely used for both ferrous and non-ferrous metals. Hardened steels, stainless steels, and titanium alloys are common in aerospace and automotive parts where durability is critical. Aluminium is ground for lightweight, tight-tolerance components. Superalloys such as Inconel, often used in turbines and energy systems, can also be efficiently processed.
2. Ceramics
Advanced ceramics are extremely hard and brittle, making them difficult to cut with standard tools. CNC grinding allows aerospace, semiconductor, and biomedical industries to machine ceramics without cracking, producing smooth finishes for seals, sensors, and substrates.
3. Plastics
High-performance plastics like PEEK, PTFE, and acrylics are used in industries such as medical devices and electronics. The process ensures accuracy without melting or deforming the material under heat.
4. Composites
Fibre-reinforced composites, including carbon fibre and fibreglass, are increasingly used in aerospace and automotive applications. CNC grinding achieves clean, accurate edges without fraying, ideal for lightweight but high-strength parts.
5. Precious Metals
Gold, silver, platinum, and other valuable materials are used in electronics, medical, and luxury applications. Grinding ensures precision while minimising waste — crucial when working with costly resources.
CNC grinding’s versatility makes it the go-to process for parts built to withstand stress, heat, or corrosive conditions.
At Kirmell, we grind a wide variety of materials from hardened steels to composites and precious metals, providing versatile solutions for complex parts.

Industries That Use CNC Grinding
The CNC grinding spans across industries where tight tolerances and flawless finishes are vital.
1. Automotive
Transmission shafts, camshafts, bearings, and injectors rely on grinding for smooth finishes that reduce friction and extend service life.
2. Medical Devices
From surgical tools to implants, grinding delivers biocompatibility, smoothness, and micron-level accuracy.
3. Tool & Die Making
Precision punches, moulds, and dies demand grinding to achieve exact tolerances, ensuring high-quality mass production.
4. Electronics & Semiconductor
Micro components, wafers, and connectors require ultra-precise grinding to function in devices like phones and computers.
5. Defense & Military
Grinding supports the production of weapons, vehicles, and other mission-critical components that cannot fail.
6. Energy Sector
Wind turbine shafts, power plant equipment, and nuclear parts depend on grinding for durability and reliability.
7. Precision Engineering
Robotics, custom machinery, and one-off designs benefit from grinding’s accuracy and flexibility.
Wherever tolerances are tight, CNC grinding delivers the consistency and reliability required.

Advantages of CNC Grinding Machines
The advantages of CNC grinding extend far beyond material removal. The process combines micron-level accuracy, versatility, and automation to meet modern industry’s toughest demands.
1. Unmatched Precision
Tolerances as fine as a few microns make grinding indispensable in aerospace, medical, and high-precision engineering.
2. Superior Surface Finishes
Grinding produces burr-free, highly polished surfaces — often eliminating the need for secondary finishing.
3. Complex Part Geometries
It can machine contours and shapes that are nearly impossible with milling or turning, making it ideal for moulds and intricate parts.
4. Hard Material Capability
Grinding efficiently handles steels, ceramics, and exotic alloys that wear out traditional tools.
5. Consistency & Repeatability
Automation ensures identical results across large runs, vital in industries where uniformity equals safety.
Design and Operational Tips
To get the best from grinding, keep these guidelines in mind:
- Design for Manufacturability – Avoid overly complex geometries if simpler alternatives exist.
- Tolerancing – Specify tolerances only as tight as necessary.
- Surface Finish Requirements – Communicate clearly to avoid rework.
- Workholding – Secure setups reduce errors.
- Tool/Wheel Selection – Use the right abrasive for the material.
- System Integration – Ensure compatibility with CAD/CAM workflows.
These tips reduce production time and cost without sacrificing quality.
Kirmell CNC Grinding Services
At Kirmell Ltd, CNC grinding is part of our precision engineering offering. Our grinding services are designed to deliver tight tolerances, smooth surface finishes, and reliable repeatability across a wide range of materials — from hardened steels and superalloys to aluminium and speciality components.
Whether you need one-off prototypes, small production runs, or high-volume manufacturing, our CNC grinding solutions ensure accuracy and efficiency. Combined with our wider capabilities in CNC machining, laser cutting, and fabrication, Kirmell provides a complete manufacturing service to meet the most demanding industry standards.
Get in touch with our team today to discuss your CNC grinding requirements or request a free quote. Let Kirmell help you achieve precision results for your complex parts
Conclusion
CNC grinding machines represent the peak of modern finishing technology. By combining abrasive grinding with the accuracy of CNC, manufacturers achieve unparalleled precision and consistency. From aerospace engines to medical devices, grinding plays a vital role in creating reliable, high-performance components.
If you need tight tolerances, smooth finishes, or hard-to-machine materials processed, precision grinding CNC is the solution.
FAQs
What is CNC grinding used for?
How does a CNC grinding machine differ from a CNC milling machine?
What materials can be ground using CNC grinding?
What types of CNC grinding machines are available?
What is the typical turnaround time for CNC grinding services?
Do you provide quotes for CNC grinding projects?
Can CNC grinding be combined with other services at Kirmell?












Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!