What Makes CNC Machining Ideal for Prototyping and Mass Production?
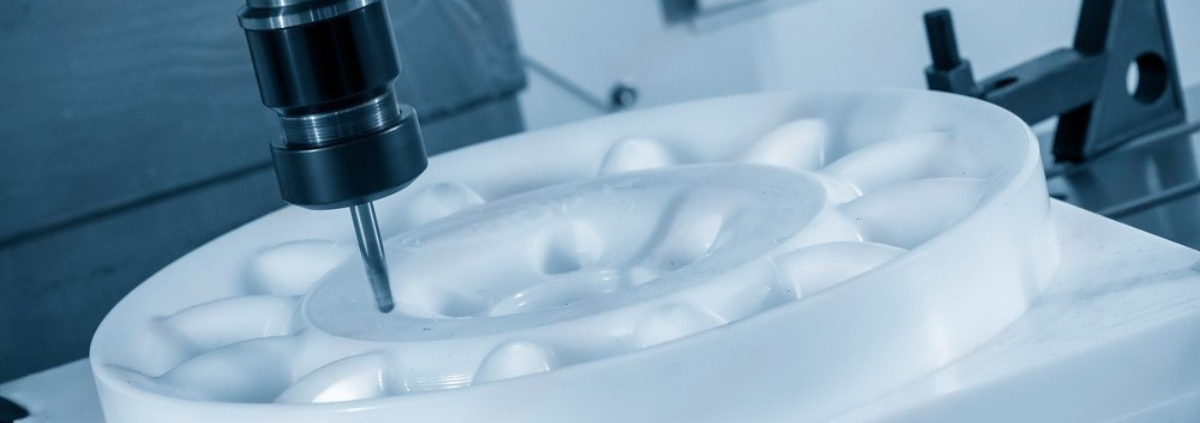
CNC machining has become a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, known for its versatility, speed, and high level of accuracy. Whether you’re building a one-off prototype or scaling up to full mass production, CNC machining consistently delivers reliable results. But what exactly makes CNC machining such a powerful choice for both ends of the production spectrum?
In this article, we’ll explore why CNC machining for prototyping and mass production continues to dominate the industry, how it supports product development, and how manufacturers provide valuable support through expert CNC machining services.
Why is CNC Machining Best for Prototyping and Mass Production
Precision and Accuracy in Every Stage
One of the standout benefits of CNC machining is its unmatched precision. CNC machines operate with digital instructions, which allow them to produce parts with extremely tight tolerances, often within ±0.01mm. This is critical during the prototyping stage when the goal is to replicate exact designs for testing and validation.
Equally, in mass production, the ability to replicate those designs hundreds or thousands of times with minimal deviation ensures product quality and uniformity, making CNC machining prototype service ideal across the board.

Speed and Efficiency
CNC prototyping is faster than many traditional methods, like manual machining or casting. Once the CAD file is ready, the design can be converted into a CNC program and processed directly on the machine, dramatically cutting down the time from concept to physical part.
This speed scales effectively in mass production too. CNC machines can run around the clock with minimal supervision, leading to higher throughput and lower labour costs. With the help of automated tool changers and multi-axis capabilities, production lines can be kept running without interruption.
At Kirmell, we operate advanced multi-axis CNC machines with automated tool changers, allowing us to deliver fast, uninterrupted production with consistent quality.
Easy Transition from Prototype to Production
A major advantage of prototype machining using CNC is that it allows a seamless transition from initial concept to production-scale manufacturing. The same CAD/CAM files used for prototypes can be adapted for full production runs with only minimal modifications.
This reduces the chances of design changes getting lost in translation between prototyping and production, cutting down development cycles and helping businesses reach the market faster.
Wide Range of Materials
CNC machines are compatible with a wide variety of materials, including metals (like aluminium, brass, stainless steel), plastics (such as ABS, nylon, and PEEK), and even composite materials. This makes prototype CNC machining extremely flexible, allowing designers to test their concepts using end-use materials.
During mass production, material options can be selected for durability, strength, or aesthetics, whatever your final application demands. Whether it’s a soft plastic prototype or a hardened steel structural part, CNC machining can handle it all.
Excellent Surface Finish and Post-Processing Compatibility
When you’re creating prototypes that need to closely resemble the final product, surface finish matters. CNC machines can deliver smooth surface finishes right off the machine, reducing the need for additional polishing or finishing.
For mass production, this also means shorter post-processing cycles. Features like threading, drilling, or engraving can be included directly into the CNC process using advanced CNC engraving machines, further cutting down time and improving accuracy.
Cost-Effectiveness
Though CNC machining might seem costly compared to some traditional prototyping techniques, it’s highly cost-effective when considering quality, speed, and reduced error margins. Especially for low-volume production or bridge tooling between prototyping and full-scale manufacturing, CNC offers an ideal balance.
In mass production, the cost per part drops significantly as quantities increase. And because of the minimal human error, waste is reduced, keeping material costs under control.
Design Flexibility and Iteration
Iterating design changes is straightforward with CNC machining. During the prototyping stage, if a tweak is needed, the engineer simply modifies the CAD model and regenerates the CNC code. This means fast design evolution and faster innovation.
When you move to mass production, this same flexibility allows for minor improvements or customer-specific variations to be implemented with minimal downtime, keeping production responsive and adaptable. Check our detailed guide on CNC Machining vs Traditional Machining.
Scalability
CNC machining is one of the most scalable manufacturing solutions. A single machine can handle a one-off CNC prototype or be one of dozens in a coordinated production environment producing thousands of parts daily.
Using tools like the CNC beam drilling machine, large and complex parts can be produced with consistent results, making CNC machining suitable for everything from electronics housings to car and automotive components.
At Kirmell, our scalable CNC machining solutions are designed to grow with your project, from initial prototype to full-scale manufacturing runs.
Practical Tips for Effective CNC Prototyping
CNC prototyping plays a vital role in transforming design ideas into tangible components that can be assessed and improved before launching full-scale production. However, to get the best results from this process, there are a few key considerations that designers and engineers should keep in mind. Here’s how to make the most of your CNC prototyping efforts:
Simplify Your Design Where Possible
It’s tempting to build a highly detailed prototype from the get-go, but simplicity often pays off, especially during early-stage development. Complex features with tight curves, intricate cavities, or deep undercuts can significantly increase both machining time and setup costs. Starting with a simplified version helps you validate the form and basic function first, saving time and resources.
Stick with Standard Tolerances Initially
Trying to achieve ultra-tight tolerances across the board can drive up both time and costs unnecessarily. Unless your application absolutely requires it, start with industry-standard tolerances, especially for non-critical features. Experienced machinists can advise you when tighter specs are essential and when standard ones will do the job just fine.
Design with CNC Tooling Limits in Mind
CNC tools, especially milling and drilling tools, have physical limitations such as tool diameter, length, and cutting angles. Features like sharp internal corners or deep, narrow slots can be difficult or impossible to machine directly. When designing your prototype, keep these tool characteristics in mind to avoid unnecessary revisions or additional steps like EDM (electrical discharge machining).
Choose an Experienced CNC Prototyping Partner
Working with a skilled and knowledgeable CNC service provider can make a significant difference. Experts understand the nuances of tool paths, material selection, and fixture design. They’ll also be able to guide you through potential design improvements and help streamline your project timeline. Companies like Kirmell Ltd offer not only technical know-how but also valuable insights into optimising designs for both prototypes and eventual production.

Use Materials Strategically
Selecting the right material for your prototype can influence both cost and performance. If the final product is made from an expensive alloy, consider using a less costly but similar alternative during early testing. This allows for evaluation of form and basic function without consuming your final-grade materials prematurely.
Learn why CNC Machining remains a core tool in modern manufacturing.
Plan for Iteration
Prototypes are rarely perfect on the first try. Build time into your development schedule for potential design tweaks and re-machining. With CNC, updates to CAD files are relatively easy to implement, so you can refine your design quickly and efficiently—but only if you’re prepared for that iterative process.
Limitations of CNC Prototyping
While CNC machining offers numerous advantages in prototyping, such as precision, speed, and material versatility, it’s not without its challenges. Understanding the limitations of CNC prototyping can help design teams make better decisions early in the development process. Below are some of the main constraints to be aware of:
Constraints on Internal Geometries
CNC machining operates by removing material from the outside of a solid block using cutting tools. As a result, creating intricate internal features, such as enclosed hollow sections or complex undercuts, can be difficult or even impossible using standard machining techniques. For parts requiring detailed internal structures, additive manufacturing methods like 3D printing may offer a more practical solution.
High Skill Requirement
Unlike some rapid prototyping methods that are plug-and-play, CNC machining demands technical knowledge. From CAD model design and tool path programming to material selection and machine operation, the process requires trained professionals. Missteps in programming or setup can lead to costly errors or wasted materials, making experience an essential asset in CNC prototyping.
Material Waste
As a subtractive manufacturing method, CNC machining involves cutting away material from a larger workpiece. This inherently generates waste, especially when using high-value metals like titanium or stainless steel. While efficient nesting and careful planning can minimise scrap, material usage is still typically higher compared to additive techniques, which build parts layer by layer.
Limited Cost Efficiency for Complex, One-Off Designs
While CNC machining excels at producing accurate prototypes, costs can rise quickly for designs with high complexity or tight tolerances. Machining a part with multiple operations or specialised tooling increases both labour and machine time. For a single prototype, these costs might not be justifiable, especially when alternative technologies like 3D printing offer quicker and cheaper turnaround for complex shapes.
Setup Time and Lead Time for Custom Parts
CNC prototyping isn’t always instant. The process involves setup time, selecting and mounting tools, configuring fixtures, calibrating machines, and generating CAM programs. For simple parts, this may not be an issue, but for custom or multi-step designs, the initial setup can extend lead times compared to faster prototyping methods.
Conclusion
CNC machining stands out as a highly versatile and reliable solution for both prototyping and mass production. Its precision, speed, material compatibility, and repeatability make it an essential tool in industries ranging from automotive and aerospace to medical devices and consumer electronics. Whether engineers are testing a single prototype or scaling up for large-volume production, CNC technology ensures quality and efficiency at every stage.
For prototyping, CNC machining offers unmatched advantages engineers can create accurate parts quickly in end-use materials, validate designs, and make iterations with minimal delays. Once the prototype is approved, transitioning to mass production is seamless, thanks to the repeatable precision and automation capabilities of CNC systems
Kirmell CNC Machining Services
At Kirmell Ltd, we specialise in high-precision CNC machining for prototyping and mass production. Whether you’re developing a new product or scaling your operations, we offer a full range of prototype CNC services tailored to your needs.
Our services include:
- CNC milling and turning
- Rapid prototyping and short-run production
- High-tolerance precision machining
- Advanced CNC engraving machines
- Full CAD/CAM support
- Material sourcing and post-processing
Based in the UK, our CNC machining services in Birmingham are trusted by leading companies across various sectors. From single custom parts to large-scale manufacturing, Kirmell delivers reliable, on-time, and high-quality results.
Contact our team today to learn how our CNC machining prototype service can accelerate your product development.
FAQs
What industries benefit most from CNC prototyping?
How fast can I get a CNC prototype?
Can I use CNC for low-volume production?
What’s the difference between CNC prototyping and 3D printing?
Do I need a 3D CAD file for CNC prototyping?












Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!